Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS), which uses various sensors (millimeter radar, laser radar, single/binocular camera, and other sensors) installed on the auto to sense the surrounding environment at any time during the driving process of the auto. And collect data, identify static and dynamic objects, descry and track, and combine the navigation map data to systematically calculate and analyze. So that the driver can be aware of possible dangers in advance, and the comfort and safety of driving can be effectively increased.
The overall ADAS system can be divided into perception layer, a decision-making layer and execution layer.
Because consumers are paying more and more attention to the active safety function of their cars. The ADAS driving assistance system, which only appeared on high-end luxury models before, has gradually become the basic configuration of many vehicles. As vehicles equipped with ADAS systems increase, in the following situations, you need to perform ADAS calibration on your car:
① After the accident is repaired, the relevant auxiliary systems need to be calibrated.
②When dismantling or reinstalling monitoring components, such as cameras, radars, and sensors, replacing the vehicle ECU, or changing the height of the vehicle, it is also necessary to calibrate the auxiliary system and other systems.
If the ADAS cannot work normally or the system has deviations or malfunctions, the system may misjudge the actual driving situation and make wrong instructions, which will affect the safe driving of the vehicle.
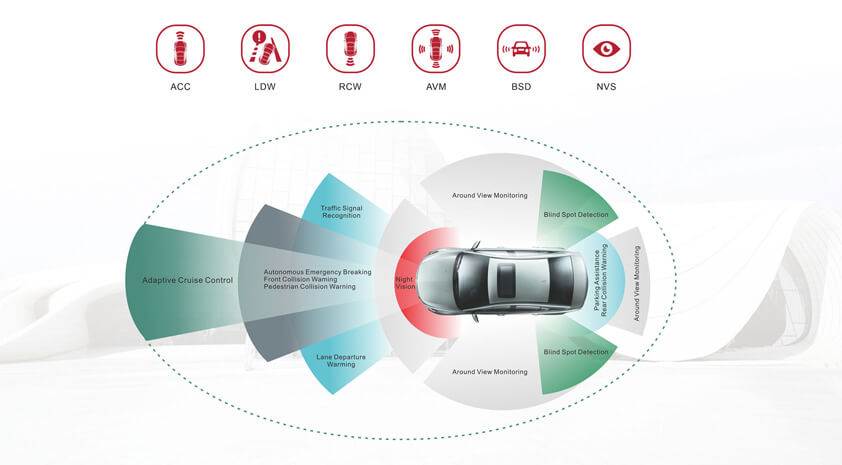
Common ADAS systems are:
While the vehicle is running, the vehicle distance sensor installed at the front of the vehicle continuously scans the road ahead of the vehicle, while the wheel speed sensor collects the vehicle speed signal.
When the distance is too small from the vehicle in front, the ACC control unit can properly brake the wheels and reduce the output power of the engine by coordinating with the brake anti-lock braking system and the engine control system to make the vehicle and the vehicle in front keep a safe distance all the time.
Forward Collision Warning also frequently uses camera sensors. By comparing the shape of the rear of the vehicle in front with the shape in the database. The algorithm calculates the time distance of the possible collision and sends an alarm to the driver in advance. The FCW system itself does not take any braking action to avoid a collision or control the vehicle.
Lane Departure Warning system is mainly composed of HUD head-up display, camera, controller and sensors. When the lane departure system is turned on, the camera will always collect the marking lines of the driving lane. Obtain the position parameters of the car in the current lane through image processing. When it is detected that the car deviates from the lane, the sensor will collect the vehicle data and the driver's operating status in time, and then the controller will send out an alarm signal. The whole process is completed in about 0.5 seconds, providing the driver with more reaction time. And if the driver turns on the turn signal and changes lanes normally, the lane departure warning system will not make any prompts.
Using the images acquired by the DMS camera, the driver's driving behavior and physiological state are detected through visual tracking, target detection, action recognition and other technologies. When the driver is fatigued, distracted, talking on the phone, smoking, not wearing a seat belt and in other dangerous situations, the system will alarm within the set time to avoid accidents. The DMS system can effectively regulate the driver's driving behavior and greatly reduce the probability of traffic accidents.
According to the classification standards introduced by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) and the National Highway Safety Administration (NHTSA). It is divided into 5 levels.
Most cars are still driven manually on the market. Humans perform dynamic driving maneuvers. However, there are corresponding systems to assist the driver. But technically speaking, the assistance system does not actively "drive" the vehicle, so it is not automated driving.
The vehicle has individual driver assistance systems, such as acceleration or deceleration. A human driver performs all other driving maneuvers. This is the lowest level of automated driving.
The vehicle has multiple driving assistance systems. The vehicle can control the steering wheel, acceleration and deceleration, and human drivers operate other driving actions.
The vehicle has driver assistance systems with the ability to "detect the environment" and can make decisions based on the information itself. But this level still requires human drivers to operate.
Under limited road and environmental conditions, human intervention is not required in most cases. However, the driver still has the option of manual control.
The driverless system performs all driving operations without human attention. It can go anywhere and do things that only experienced human drivers can do. Drive on all roads and under environmental conditions.
Return